CloudWatch Agent Setup Guide for EC2 Linux
The CloudWatch agent is AWS’s unified monitoring tool that collects system metrics and application logs from EC2 instances. Unlike manual SSH access, the CW agent provides centralized log management across multiple servers, making it essential for production environments and auto-scaling groups where instances may terminate before logs can be retrieved.
This guide walks you through the process of installing the CloudWatch agent on Amazon Linux 2023 and configuring it to stream application logs to CloudWatch.
CloudWatch Agent Setup Prerequisites
Before installing the agent, verify your EC2 instance has an IAM role with the CloudWatchAgentServerPolicy managed policy. This policy grants the agent permission to publish logs and metrics.
CloudWatch Agent Installation
Once your instance has the prerequisite permissions to CloudWatch, we can install the CW Agent if it hasn’t already been created. You can verify if the agent is already installed using the agent version command.
SSH into your EC2 instance and download the CW Agent package:
cd /tmp wget https://s3.amazonaws.com/amazoncloudwatch-agent/amazon_linux/amd64/latest/amazon-cloudwatch-agent.rpm sudo rpm -U amazon-cloudwatch-agent.rpm
Verify the Installation:
/opt/aws/amazon-cloudwatch-agent/bin/amazon-cloudwatch-agent -version
CloudWatch Agent Setup Configuration
Once the Agent has been successfully installed, create a new configuration file that tells the agent which log files to monitor:
sudo vi /opt/aws/amazon-cloudwatch-agent/etc/amazon-cloudwatch-agent.jsonYou can paste the following content into the config file to stream SFTP Gateway log files to CloudWatch:
{
"logs": {
"logs_collected": {
"files": {
"collect_list": [
{
"file_path": "/var/log/sftpgw/cloudinit.log",
"log_group_name": "sftpgw-{instance_id}",
"log_stream_name": "cloudinit-{instance_id}",
"retention_in_days": 60,
"timestamp_format": "%b %d %H:%M:%S"
},
{
"file_path": "/opt/sftpgw/log/application*.log",
"log_group_name": "sftpgw-{instance_id}",
"log_stream_name": "application-{instance_id}",
"retention_in_days": 60,
"timestamp_format": "%b %d %H:%M:%S"
},
{
"file_path": "/opt/sftpgw/log/sftp-audit*.log",
"log_group_name": "sftpgw-{instance_id}",
"log_stream_name": "audit-{instance_id}",
"retention_in_days": 60,
"timestamp_format": "%b %d %H:%M:%S"
}
]
}
}
}
}
For detailed SFTP Gateway-specific setup instructions, see our guide to setting up log streaming to CloudWatch.
For general Linux system logs, configure the agent to monitor common log locations, such as logs located in /var/log:
{
"file_path": "/var/log/secure",
"log_group_name": "/aws/ec2/system/secure",
"log_stream_name": "{instance_id}",
"retention_in_days": 90,
"timestamp_format": "%b %d %H:%M:%S"
},
Starting the Agent
Apply your configuration and start the agent:
sudo /opt/aws/amazon-cloudwatch-agent/bin/amazon-cloudwatch-agent-ctl -a fetch-config -m ec2 -c file:/opt/aws/amazon-cloudwatch-agent/etc/amazon-cloudwatch-agent.json -s
Enable automatic startup on reboot:
sudo systemctl enable amazon-cloudwatch-agent
Monitor the agent logs to confirm it’s correctly streaming logs into CloudWatch:
sudo tail -f /opt/aws/amazon-cloudwatch-agent/logs/amazon-cloudwatch-agent.log
You’ve now successfully configured log streaming to CloudWatch on your EC2 instance.
View the logs in CloudWatch
Now that you’ve confirmed the logs are being streamed to CloudWatch, we can check them out in the AWS Console.
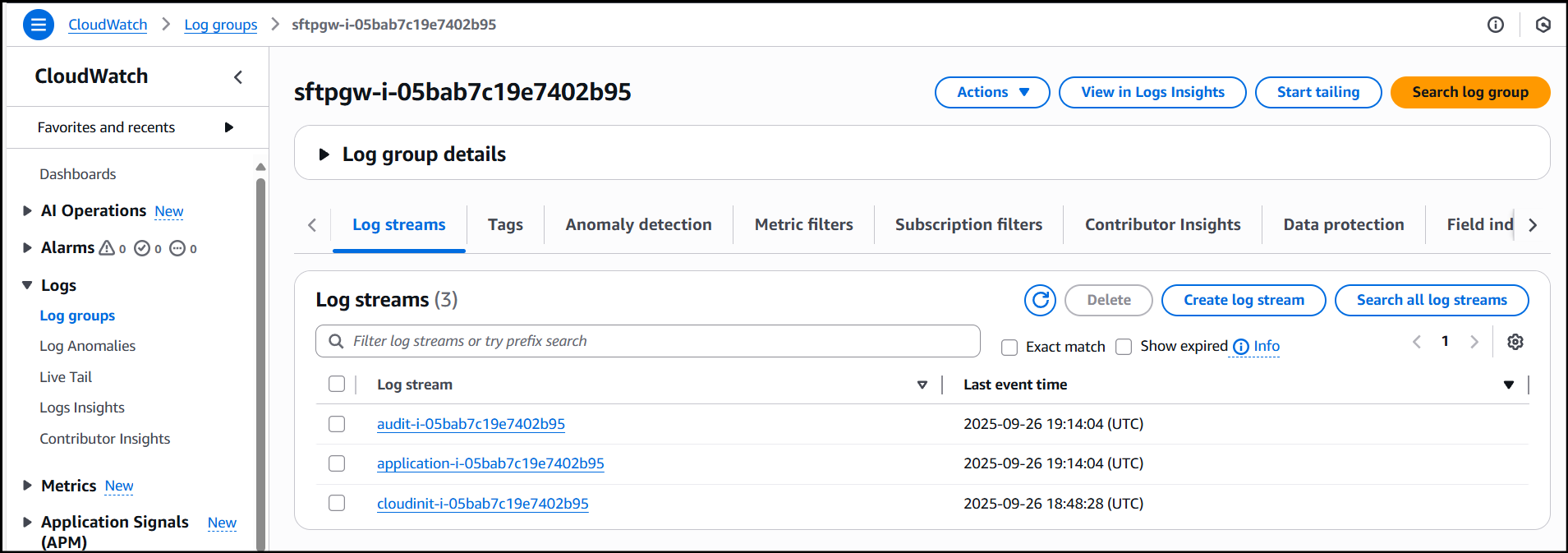
Navigate to CloudWatch and under the Logs section, click into Log groups. Here, we can search for the ID of our EC2 instance from which we’re streaming the logs, as the log group takes the name of your EC2 instance by default. Click into the log group name and you’ll see the current log files being streamed to CloudWatch:
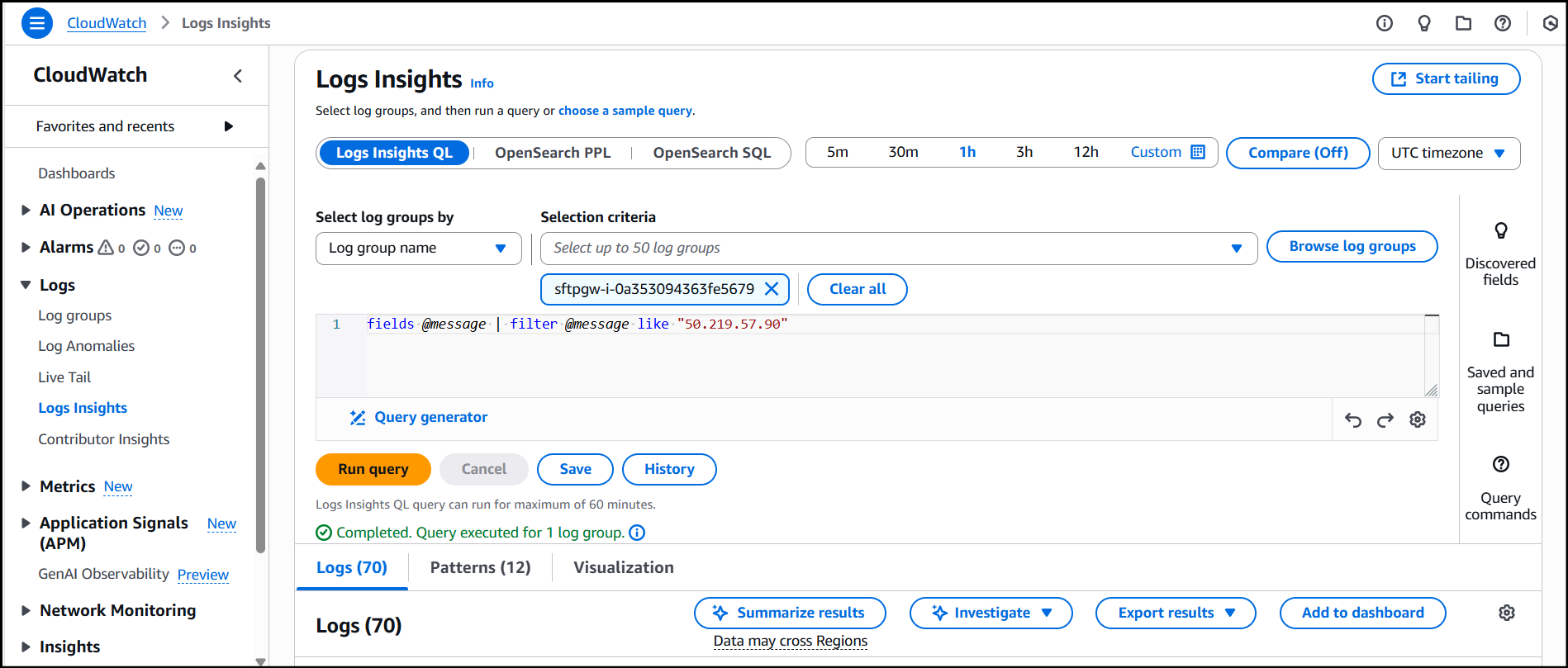
To perform Log Queries, click into View in Log Insights. Here, you’re able to search for specific keywords such as usernames and IP Addresses of clients connecting to the server or names of files and services which are being used by the instance.
Using a simple query such as the one below, you can search for specific keywords:
fields @message | filter @message like "keyword_here"
In my example, I am searching for a specific IP Address, which shows up in 70 logs across my Log group:
Configuration Considerations with CloudWatch Agent Setup
Consider adding metric filters to extract custom metrics from your logs, or configure alarms to alert on specific error patterns detected by the CloudWatch agent.
Set retention periods in your agent configuration according to the importance of the logs. Security logs typically require a retention period of 90 days or more for compliance, while application or debug logs may only require a retention period of 14-30 days.
For enterprise deployments, store your CloudWatch agent configuration in AWS Systems Manager Parameter Store to enable centralized management across multiple EC2 instances.